11 (number)
| 11 | |
|---|---|
| Cardinal | eleven |
| Ordinal | 11th (eleventh) |
| Factorization | prime |
| Divisors | 1, 11 |
| Roman numeral | XI |
| Greek Prefix | hendeca-/hendeka- (from Greek) |
| Latin Prefix | undeca- (from Latin) |
| Binary | 10112 |
| Octal | 138 |
| Duodecimal | B12 |
| Hexadecimal | B16 |
11 (eleven i/ɨˈlɛvɨn/ or /iˈlɛvɛn/) is the natural number following 10 and preceding 12.
Eleven is the first number which cannot be counted with a human's ten fingers. In English, it is the smallest positive integer requiring three syllables and the largest prime number with a single-morpheme name. Its etymology originates from a Germanic compound ainlif meaning "one left".[1]). It is also the second number in the "teens."
Contents[hide] |
In mathematics
Eleven is the 5th smallest prime number. It is the smallest two-digit prime number in the decimal base; as well as, of course, in undecimal (where it is the smallest two-digit number). It is also the smallest three-digit prime in ternary, and the smallest four-digit prime in binary, but a single-digit prime in bases larger than eleven, such as duodecimal, hexadecimal, vigesimal and sexagesimal. 11 is the fourth Sophie Germain prime, the third safe prime, the fourth Lucas prime, the first repunit prime, and the second good prime. Although it is necessary for n to be prime for 2n − 1 to be a Mersenne prime, the converse is not true: 211 − 1 = 2047 which is 23 × 89. The next prime is 13, with which it comprises a twin prime. 11 is an Eisenstein prime with no imaginary part and real part of the form 3n − 1. Displayed on a calculator, 11 is a strobogrammatic prime and a dihedral prime because it reads the same whether the calculator is turned upside down or reflected on a mirror, or both.
If a number is divisible by 11, reversing its digits will result in another multiple of 11. As long as no two adjacent digits of a number added together exceed 9, then multiplying the number by 11, reversing the digits of the product, and dividing that new number by 11, will yield a number that is the reverse of the original number. (For example: 142,312 x 11 = 1,565,432. 2,345,651 / 11 = 213,241.)
Because it has a reciprocal of unique period length among primes, 11 is the second unique prime. 11 goes into 99 exactly 9 times, so vulgar fractions with 11 in the denominator have two digit repeating sequences in their decimal expansions. Multiples of eleven by one-digit numbers all have matching double digits: 00 (=0), 11, 22, 33, 44, etc. Bob Dorough, in his Schoolhouse Rock song "The Good Eleven", called them "Double-digit doogies" (soft g). Eleven is the Aliquot sum of one number, the discrete semiprime 21 and is the base of the 11-aliquot tree.
As 11 is the smallest factor of the first eleven terms of the Euclid–Mullin sequence, it is the twelfth term.
An eleven-sided polygon is called a hendecagon or undecagon.
In both base 6 and base 8, the smallest prime with a composite sum of digits is 11.
Any number b+1 is written as "11b" in base b, so 11 is trivially a palindrome in base 10. However 11 is a strictly non-palindromic number.
In base 10, there is a simple test to determine if an integer is divisible by 11: take every digit of the number located in odd position and add them up, then take the remaining digits and add them up. If the difference between the two sums is a multiple of 11, including 0, then the number is divisible by 11.[2] For instance, if the number is 65,637 then (6 + 6 + 7) - (5 + 3) = 19 - 8 = 11, so 65,637 is divisible by eleven. This technique also works with groups of digits rather than individual digits, so long as the number of digits in each group is odd, although not all groups have to have the same number of digits. For instance, if one uses three digits in each group, one gets from 65,637 the calculation (065) - 637 = -572, which is divisible by eleven.
Another test for divisibility is to separate a number into groups of two consecutive digits (adding a leading zero if there is an odd number of digits), and then add up the numbers so formed; if the result is divisible by eleven, the number is divisible by eleven. For instance, if the number is 65,637, 06 + 56 + 37 = 99, which is divisible by eleven, so 65,637 is divisible by eleven. This also works by adding a trailing zero instead of a leading one: 65 + 63 + 70 = 198, which is divisible by eleven. This also works with larger groups of digits, providing that each group has an even number of digits (not all groups have to have the same number of digits).
An easy way of multiplying numbers by 11 in base 10 is: If the number has:
- 1 digit - Replicate the digit (so 2 x 11 becomes 22).
- 2 digits - Add the 2 digits together and place the result in the middle (so 47 x 11 becomes 4 (11) 7 or 4 (10+1) 7 or (4+1) 1 7 or 517).
- 3 digits - Keep the first digit in its place for the result's first digit, add the first and second digits together to form the result's second digit, add the second and third digits together to form the result's third digit, and keep the third digit as the result's fourth digit. For any resulting numbers greater than 9, carry the 1 to the left. Example 1: 123 x 11 becomes 1 (1+2) (2+3) 3 or 1353. Example 2: 481 x 11 becomes 4 (4+8) (8+1) 1 or 4 (10+2) 9 1 or (4+1) 2 9 1 or 5291.
- 4 or more digits - Follow the same pattern as for 3 digits.
In base 10, 11 is the smallest integer that is not a Nivenmorphic number.
In base thirteen and higher bases (such as hexadecimal), eleven is represented as B, where ten is A. In duodecimal, however, eleven is sometimes represented as E and ten as T.
Eleven is a Størmer number, a Heegner number, and a Mills prime.
There are 11 orthogonal curvilinear coordinate systems (to within a conformal symmetry) in which the 3-variable Helmholtz equation can be solved using the separation of variables technique.
See also 11-cell.
Eleven of the thirty-five hexominoes can be folded to form cubes. Eleven of the sixty-six octiamonds can be folded to form octahedra.
The partition numbers (sequence A000041 in OEIS) contain much more multiples of eleven than the one-eleventh one would expect.
According to David A. Klarner, a leading researcher and contributor to the study of polyominoes, it is possible to cut a rectangle into an odd number of congruent, non-rectangular polyominoes. Eleven is the smallest such number, the only such number that is prime, and the only such number that is not a multiple of three.
11 raised to the n power is the nth row of Pascal's Triangle. (This works for any base)
List of basic calculations
| Multiplication | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 1000 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
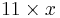 |
11 | 22 | 33 | 44 | 55 | 66 | 77 | 88 | 99 | 110 | 121 | 132 | 143 | 154 | 165 | 176 | 187 | 198 | 209 | 220 | 231 | 242 | 253 | 264 | 275 | 550 | 1100 | 11000 |
| Division | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | ||||||
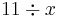 |
11 | 5.5 | 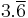 |
2.75 | 2.2 | 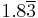 |
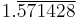 |
1.375 | 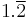 |
1.1 |
| 1 | 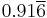 |
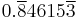 |
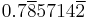 |
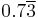 |
||||||
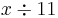 |
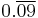 |
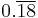 |
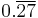 |
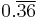 |
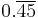 |
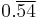 |
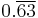 |
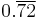 |
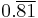 |
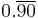 |
| 1 | 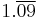 |
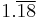 |
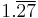 |
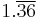 |
| Exponentiation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
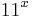 |
11 | 121 | 1331 | 14641 | 161051 | 1771561 | 19487171 | 214358881 | 2357947691 | 25937421601 | 285311670611 | 3138428376721 | 34522712143931 | |
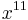 |
1 | 2048 | 177147 | 4194304 | 48828125 | 362797056 | 1977326743 | 8589934592 | 31381059609 | 100000000000 | 285311670611 | 743008370688 | 1792160394037 |
| Radix | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 10000 | 100000 | 1000000 | |||
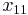 |
1 | 5 | 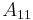 |
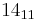 |
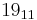 |
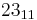 |
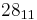 |
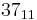 |
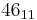 |
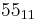 |
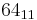 |
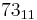 |
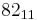 |
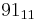 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
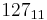 |
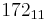 |
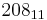 |
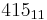 |
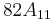 |
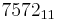 |
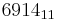 |
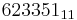 |
List of basic operations that make 11
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 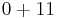 |
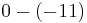 |
N/A | N/A |
| 1 | 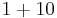 |
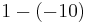 |
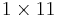 |
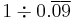 |
| 2 | 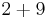 |
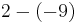 |
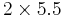 |
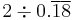 |
| 3 | 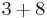 |
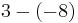 |
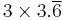 |
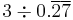 |
| 4 | 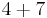 |
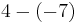 |
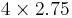 |
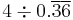 |
| 5 | 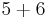 |
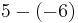 |
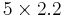 |
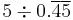 |
| 6 | 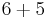 |
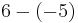 |
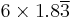 |
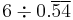 |
| 7 | 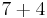 |
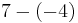 |
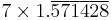 |
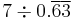 |
| 8 | 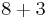 |
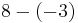 |
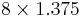 |
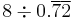 |
| 9 | 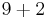 |
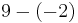 |
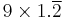 |
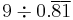 |
| 10 | 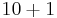 |
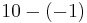 |
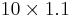 |
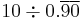 |
| 11 | 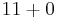 |
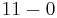 |
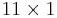 |
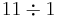 |
In science
- The atomic number of sodium.
- In chemistry, Group 11 includes the three coinage metals copper, silver, and gold known from antiquity. It also includes the superheavy element roentgenium, which was discovered only recently.
- The number of spacetime dimensions in M-theory.
Astronomy
- The approximate periodicity of a sunspot cycle is 11 years.
- Messier object M11, a magnitude 7.0 open cluster in the constellation Scutum, also known as the Wild Duck Cluster.
- The New General Catalogue object NGC 11, a spiral galaxy in the constellation Andromeda
- The Saros number of the solar eclipse series which began on -2511 December 26 and ended on -1158 March 18. The duration of Saros series 11 was 1352.2 years, and it contained 76 solar eclipses.
- The Saros number of the lunar eclipse series which began on -2389 June 19 and ended on -1037 September 8. The duration of Saros series 11 was 1352.2 years, and it contained 76 lunar eclipses.
In religion
After Judas Iscariot was disgraced, the remaining apostles of Jesus were sometimes described as "the Eleven"; this occurred even after Matthias was added to bring the number to twelve, as in Acts 2:14.
Eleven is a spiritually significant number in Thelema.
In music
- The interval of an octave and a fourth is an eleventh. A complete eleventh chord has almost every note of a diatonic scale.
- The number of thumb keys on a bassoon, not counting the whisper key. (A few bassoons have a twelfth thumb key.)
- In the mockumentary This Is Spinal Tap, Spinal Tap's amplifiers go up to eleven.
- In Igor Stravinsky's The Rite of Spring, there are eleven consecutive repetitions of the same chord.
- In Tool's song Jimmy, and in Negativland's song Time Zones the number eleven is heard numerous times in the lyrics.
- "Eleven pipers piping" is the gift on the eleventh day of Christmas in the carol "The Twelve Days of Christmas"
- The Eleven is a song by The Grateful Dead.
In sports
- There are eleven players on a soccer team on the field at a time as well as in a cricket team. Within a school or college, the phrase first eleven (or first XI) - often "first football XI" and "first cricket XI" - generally refers to the first (best) team currently playing. Other teams are often referred to as "the second XI" etc.
- Also in soccer, in the German language (and others like Italian - "gli undici metri" -, countries that predominantly use the metric system) a penalty kick is referred to as "Elfmeter" because the penalty spot is approximately 11m (precisely 12 yards) from the goal line. Historically, in the Pyramid formation that position names are taken from, a left wing-forward in football wears number 11. In the modern game, especially using the 4-4-2 formation, it is worn by a left-sided midfielder. Less commonly a striker will wear the shirt.
- There are eleven players in a field hockey team. The player wearing 11 will usually play on the left-hand side, as in soccer.
- An American football team also has eleven players on the field at one time during play. 11 is also worn by quarterbacks, kickers, punter and wide receivers in American football's NFL.
- In most rugby league competitions (but not the European Super League, which uses static squad numbering), one of the starting second-row forwards wears the number 11.
- In rugby union, the starting left wing wears the 11 shirt.
- In cricket, the eleventh batsman is usually the weakest batsman, at the end of the tail. He is primarily in the team for his bowling abilities.
- The jersey number 11 has been retired by several North American sports teams in honor of past playing greats or other key figures:
- In Major League Baseball:
- The Chicago White Sox, for Hall of Famer Luis Aparicio. Current White Sox shortstop Omar Vizquel, like Aparicio a Venezuelan, wears the number with Aparicio's blessing.
- The Detroit Tigers, for Hall of Fame manager Sparky Anderson.
- The Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim, for Jim Fregosi, who played for the team in its former incarnations as the Los Angeles Angels and California Angels, and also managed the California Angels.
- The Pittsburgh Pirates, for Hall of Famer Paul Waner.
- The San Francisco Giants, for Hall of Famer Carl Hubbell, honoring the number's retirement when the team was known as the New York Giants.
- The Seattle Mariners have yet to retire any numbers, but have not issued #11 since the retirement of Edgar Martínez at the end of the 2004 season.
- The Cincinnati Reds have not yet retired #11, but have not issued it since the retirement of Barry Larkin after the 2004 season.
- In the NBA:
- The Detroit Pistons, for Hall of Famer Isiah Thomas.
- The Sacramento Kings, for Hall of Famer Bob Davies, honoring the number's retirement when the team was known as the Rochester Royals.
- The Washington Wizards, for Hall of Famer Elvin Hayes, who played for the team in its past incarnations as the Baltimore, Capital, and Washington Bullets.
- In the NFL:
- The New York Giants, for Phil Simms.
- In the NHL:
- The Buffalo Sabres, for Hall of Famer Gilbert Perreault.
- The Edmonton Oilers and New York Rangers, for Hall of Famer Mark Messier.
- The St. Louis Blues, for Brian Sutter.
- The Washington Capitals, for Hall of Famer Mike Gartner.
- In Major League Baseball:
In the military
- The number of guns in a gun salute to U.S. Army, Air Force and Marine Corps Brigadier Generals, and to Navy and Coast Guard Rear Admirals Lower Half.
- The Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) designator given to US Army Infantry Officer as well as to enlisted personnel (AKA 11 MOS Series, or 11B, 11C, 11D, 11H, 11M, etc.)
- The number of General Orders for Sentries in the Marine Corps and United States Navy.
- A page in the Service Record Book of an enlisted Marine for writing down disciplinary actions.
- World War I ended with an Armistice on November 11, 1918, which went into effect at 11:00 am-the 11th hour on the 11th day of the 11th month of the year. Armistice Day is still observed on November 11 of each year, although it is now called Veterans Day in the United States and Remembrance Day in the Commonwealth of Nations and parts of Europe.
In computing
- In Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Konqueror for KDE, Google Chrome and Internet Explorer for Windows, the function key F11 key toggles full screen viewing mode. In Mac OS X, F11 hides all open windows.
- The windowing system for Unix computers is known as X11.
- Computers of the PDP-11 series from Digital Equipment Corporation were informally referred to as "elevens".
Canada
- The stylized maple leaf on the Flag of Canada has eleven points.
- The Canadian one-dollar coin is a hendecagon, an eleven-sided polygon.
- Clocks depicted on Canadian currency, for example the Canadian fifty-dollar bill, show 11:00.
- Eleven denominations of Canadian currency are produced in large quantities.
- Due to Canada's federal nature, eleven legally distinct Crowns effectively exist in the country, with the Monarch being represented separately in each province, as well as at the federal level.
In other fields
- The number of incarnations of The Doctor in BBC sci-fi series Doctor Who is eleven.
- Three films -- Ben-Hur (1959), Titanic (1997), and The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King (2003) -- have each won eleven Academy Awards, including Best Picture of their respective years.
- The number eleven is important in numerology, as it is the first of the Master Numbers.
- Being only one hour before 12:00—midnight—the eleventh hour means the last possible moment to take care of something, and often implies a situation of urgent danger or emergency (see Doomsday clock).
- In Astrology, Aquarius is the 11th astrological sign of the Zodiac.
- Ocean's Eleven is the name of two American films.
- In Basque, hamaika ("eleven") has the double meaning of "infinite", probably from amaigabe, "endless", as in Hamaika aldiz etortzeko esan dizut! ("I told you infinite/eleven times to come!").
- American Airlines flight 11, a Boston-Los Angeles flight which crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center after being hijacked by terrorists in New York City, New York on September 11, 2001.
- The number 11 bus is a low-cost way of sightseeing in London
- In the game of blackjack, an Ace can be counted as either one or eleven, whichever is more advantageous for the player.
- 11 is the number of the French department Aude.
- In the anime series Code Geass, Japan is known as Area 11 of the Brittanian Empire.
Historical years
11 A.D., 11 B.C., 1911, 2011, etc.
See also
References
- ^ "eleven". Online Etymology Dictionary. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=eleven. Retrieved 2011-11-11.
- ^ Higgins, Peter (2008). Number Story: From Counting to Cryptography. New York: Copernicus. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-84800-000-1.